rationalism international relations
In other words persons are to achieve their goals under certain conditions. Ultimately the logic of survival of the nation-state as its central and ultimate goal makes sense.

Pdf Constructivist Approaches In International Relations Theory Puzzles And Promises Semantic Scholar
For realism whether its focus is upon the international system or upon its constituents other states are actors from which no absolutely settled pattern of policy can be expected and with which no necessarily enduring interests are shared.

. The rationalist research program has increasingly been applied to the study of international relations in Asia where the interpretive research program is still dominant. Rationalism in explaining international political life because solid and well-defined self-interests formed by costbenefit analysis can lead actors to forsake their normative values and identities. Rationality in International Relations Miles Kahler The role of reason in international relations has been contested since the eighteenth century.
Trust as a rational choice calculation as a social. There are according to the rationalists certain rational principlesespecially in logic and mathematics and even in ethics. Its application allows policymakers to.
The essay is composed of three sections. The construction of a sphere of calculated state action raison detat and an image of the balance of power suggested an Enlightenment equilibrium as compre- hensible to human reason as a clockwork. Rationalism in Western philosophy the view that regards reason as the chief source and test of knowledge.
International relations portal Rationalism in politics is often seen as the midpoint in the three major political viewpoints of realism rationalism and internationalism. Parallel to a view of international relations in which egoistic units seek material gains rationalists identify as economic libertarians at a much higher rate than non-rationalists. In the rational choice approach individuals are seen as motivated by the wants or goals that express their preferences as well as other incentives like reward or promise of reward Orji2009 p.
In the rationalist theories of the International Relations this gap is often filled by the adoption of a second axiom defending that the basic objective of any state is its survival in the international anarchic environment. The Rational Choice theory also known as Rational Decision Making Model RDMM is widely used to scrutinize foreign policy decision making Kahler 1998. In philosophy rationalism is the epistemological view that regards reason as the chief source and test of knowledge or any view appealing to reason as a source of knowledge or justification.
It was only relatively recently that IR scholars began to probe what trust really is how it can be studied and how it affects state relations. Whereas Realism and Internationalism are both on ends of the scale rationalism tends to occupy the middle ground on most issues and finds compromise between these two conflicting points of view. Rationalism and reflectivism whereat the former rubric differs among others in realist as well as liberal approaches.
The notion that race is a significant factor in international relations sits uneasily then with both realism and rationalism. Holding that reality itself has an inherently logical structure the rationalist asserts that a class of truths exists that the intellect can grasp directly. Rationalist models have faced four persistent sets of critics as the research program of international relations has evolved.
Broadly spoken IR-theories can be categorized into two big opposing groups. Under neorealisms structural constraints of international competition and selection agents rationality may appear superfluous. The construction of a sphere of calculated state action raison detat and an image of the balance of power suggested an Enlightenment equilibrium as compre-hensible to human reason as a clockwork.
The rationalistconstructivist debate is an ontological debate within international relations theory between rationalism and constructivism. The rationalist program is founded upon objective ontology contingent agent-structure epistemology and the logic of consequence. They point to current international organizations most notably the United Nations and point out that these organizations leave a lot to be desired and in some cases do more harm than good.
In the discipline of International Relations exist a great many of different theories which are drawn upon to analyze a certain circumstance. The Rationalism depends on the objective processes and the preferences of many different people with their inherent values ideals prejudices etc. Rationalist theories embrace positivism to a certain extent which means they believe that the practice of IR can be reduced to simple and observable systemic rules and laws which their theories aim to document.
Rationality in International Relations Miles Kahler The role of reason in international relations has been contested since the eighteenth century. Believers of Rationalism believe that multinational and multilateral organizations have their place in the world order but not that a world government would be feasible. Within the realist school of international relations a prevailing view holds that the anarchic structure of the international system invariably forces the great powers to seek security at one anothers expense dooming even peaceful.
Rationalism assumes that the most important and in fact the only entities dictating international relations are nation states and that these nation states are engaged in a zero-sum game of diplomacy and war in which the goals of every nation state is eventual dominance above all others so that international relations are dictated almost. In the first section I explore the major differences between rationalism and constructivism and. This systemic approach attempts to mirror the natural sciences in dismissing non-observable and therefore non-testable factors.
Thus it was later criticized by reflectivists that rationalism is not the best approach to understand the international relations. In the process three distinct ways of theorising trust in IR have emerged. In IR contexts rationalism can be defined as formal and informal applications of rational choice theory to IR questions or any work developed in the tradition of microeconomic theory Fearon and Wendt 2002 p.
Trust is a core concept in International Relations IR representing a key ingredient in state relations. More formally rationalism is defined as a methodology or a theory in which the criterion of the truth is not sensory but intellectual and deductive.

Political Science And International Relations Main Directions Of
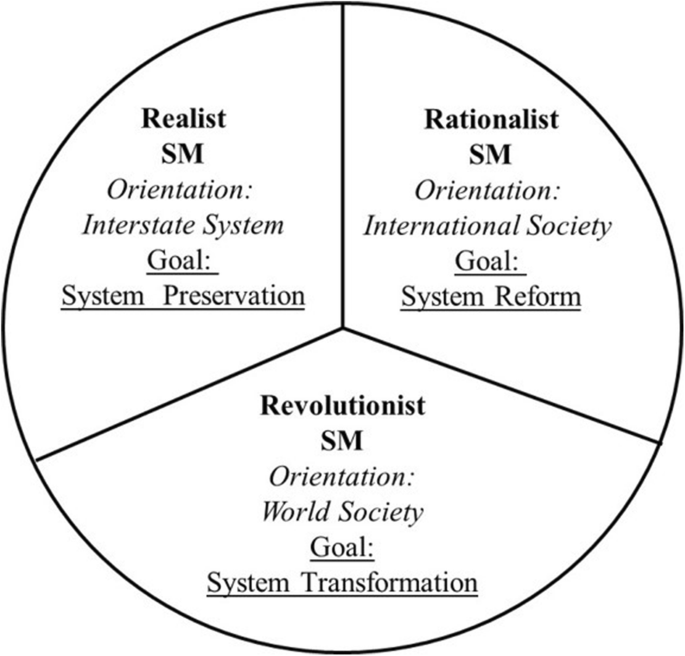
Social Movements And International Relations A Relational Framework Springerlink

Amazon Com Trust In International Relations Rationalist Constructivist And Psychological Approaches Routledge Global Cooperation Series 9780367820985 Haukkala Hiski Van De Wetering Carina Vuorelma Johanna Books

Pdf Foreign Policy Of Lithuania Linking Theory To Practice Semantic Scholar

Realism Rationalism And Revolutionism In Iran S Foreign Policy The West The State And Islam Semantic Scholar

Table 1 From How To Combine Rationalist And Constructivist Accounts Of International Politics Building Bridges On Terra Firma Semantic Scholar

Rational Theory Of International Politics Princeton University Press

Amazon Com Rationality And The Analysis Of International Conflict Cambridge Studies In International Relations Series Number 19 9780521398107 Nicholson Michael Books

Presented By Yu Seunghee Zhang Luan Ppt Video Online Download

History Of The Discipline Of International Relations Timeline Timeto

What Rationalist Approaches In Ir Contribute Grin
What Is The Diference Between Rationalism Realism And Idealism Quora

Theories Of Colonial Encounters In International Relations 41 Download Table

Realism Rationalism And Revolutionism In Iran S Foreign Policy The West The State And Islam Semantic Scholar

Pdf The English School International Relations And Progress Semantic Scholar

2 Fundamentals In International Relations Rationalism And Materialism Ab Foreign Service Studocu

Table 2 From How To Combine Rationalist And Constructivist Accounts Of International Politics Building Bridges On Terra Firma Semantic Scholar

Social Movements And International Relations A Relational Framework Springerlink

Liberalism Radical Theories John Lee Department Of Political Science Florida State University Ppt Download
0 Response to "rationalism international relations"
Post a Comment